Setting investment goals
Setting goals is an important part of financial planning. Before you invest your money, you should spend some time considering and setting your personal goals. For example, do you want to retire early? Would you like to start your own business soon? Do you need to pay for a child’s college education? Would you like to buy or build a new house? In addition to these, there are several other considerations that can help you and your financial professional develop an appropriate plan.
Think about your time horizon
One of the first questions you should ask yourself in setting your investment goals is “When will I need the money?” Will it be in 3 years or 30? Your time horizon for each of your financial goals will have a significant impact on your investment strategy.
The general rule is: The longer your time horizon, the more risky (and potentially more lucrative) investments you may be able to make. Many financial professionals believe that with a longer time horizon, you can ride out fluctuations in your investments for the potential of greater long-term returns. On the other hand, if your time horizon is very short, you may want to concentrate your investments in less risky vehicles because you may not have enough time to recoup losses should they occur.
Understand your risk tolerance
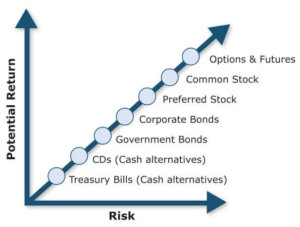
Another important question is “What is my investment risk tolerance?” How do you feel about the potential of losing your hard-earned money? Many investors would forgo the possibility of a large gain if they knew there was also the possibility of a large loss. Other investors are more willing to take on greater risk to try to achieve a higher return. You can’t completely avoid risk when it comes to investing, but it’s possible to manage it.
Almost universally, when financial professionals or the media talk about investment risk, their focus is on price volatility. Advisors label as aggressive or risky an investment whose price has been prone to dramatic ups and downs in the past, or that involves substantial uncertainty and unpredictability. Assets whose prices historically have experienced a narrower range of peaks and valleys are considered more conservative.
In general, the risk-reward relationship makes sense to most people. After all, no sensible person would make a higher-risk investment without the prospect of a higher reward for taking that risk. That is the tradeoff. As an investor, your goal is to maximize returns without taking on more risk than is necessary or comfortable for you. If you find that you can’t sleep at night because you’re worrying about your investments, you’ve probably assumed too much risk. On the other hand, returns that are too low may leave you unable to reach your financial goals.
The concept of risk tolerance refers not only to your willingness to assume risk but also to your financial ability to endure the consequences of loss. That has to do with your stage in life, how soon you’ll need the money, and your financial goals.
Remember your liquidity needs
Liquidity refers to how quickly you can convert investments into cash. Real estate, for example, tends to be relatively illiquid; it can take a very long time to sell. Publicly traded stock, on the other hand, tends to be fairly liquid.
Your need for liquidity will affect the types of investments you might choose to meet your goals. For example, if you have an emergency fund, you’re in good health, and your job is secure, you may be willing to hold some less liquid investments that may have higher potential for gain. However, if you have two children going to college in the next couple of years, you probably don’t want all of their tuition money invested in less liquid assets.
Also, having some relatively liquid investments may help protect you from having to sell others when their prices are down.
Copyright 2006- Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved.
Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. does not provide investment, tax, or legal advice. The information presented here is not specific to any individual’s personal circumstances.
To the extent that this material concerns tax matters, it is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, by a taxpayer for the purpose of avoiding penalties that may be imposed by law. Each taxpayer should seek independent advice from a tax professional based on his or her individual circumstances.
These materials are provided for general information and educational purposes based upon publicly available information from sources believed to be reliable—we cannot assure the accuracy or completeness of these materials. The information in these materials may change at any time and without notice.
*Non-deposit investment products and services are offered through CUSO Financial Services, L.P. (“CFS”), a registered broker-dealer (Member FINRA / SIPC) and SEC Registered Investment Advisor. Products offered through CFS: are not NCUA/NCUSIF or otherwise federally insured, are not guarantees or obligations of the credit union, and may involve investment risk including possible loss of principal. Investment Representatives are registered through CFS. Coastal Federal Credit Union has contracted with CFS to make non-deposit investment products and services available to credit union members.
CFS representatives do not provide tax or legal guidance. For such guidance please consult with a qualified professional. Information shown is for general illustration purposes and does not predict or depict the performance of any investment or strategy. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Trust Services are available through MEMBERS Trust Company. CFS* is not affiliated with Members Trust Company.






