Couples who have opposite philosophies regarding saving and spending often have trouble finding common ground, and money arguments frequently erupt. But you can learn to work with — and even appreciate — your financial differences.
Money habits run deep
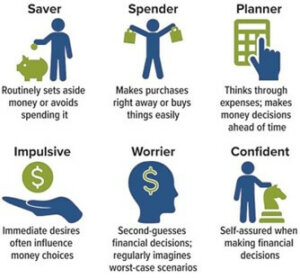
If you’re a saver, you prioritize having money in the bank and investing in your future. You probably hate credit card debt and spend money cautiously. Your spender spouse may seem impulsive, prompting you to think, “Don’t you care about our future?” But you may come across as controlling or miserly to your spouse who thinks, “Just for once, can’t you loosen up? We need some things!”
Such different outlooks can lead to mistrust and resentment. But are your characterizations fair? Money habits run deep, and have a lot to do with how you were raised and your personal experience.
Instead of assigning blame, focus on finding out how each partner’s financial outlook evolved.
Saving and spending actually go hand in hand. Whether you’re saving for a vacation, a car, college, or retirement, your money will eventually be spent on something. You just need to decide together how and when to spend it.
Talk through your differences Sometimes couples avoid talking about money because they are afraid to argue. But scheduling regular money meetings could give you more insight into your finances and provide a forum for handling disagreements, helping you avoid future conflicts.
You might not have an equal understanding of your finances, so start with the basics. How much money is coming in and how much is going out? Next, work on discovering what’s important to each of you.
To help ensure a productive discussion, establish some ground rules. For example, you might set a time limit, insist that both of you come prepared, and take a break if the discussion becomes too heated.
Communication and compromise are key. Don’t just assume you know what your spouse is thinking — ask, and keep an open mind.
Here are some questions to get started.
- What does money represent to you? Security? Freedom? The opportunity to help others?
- What are your short-term and long-term savings goals? Why are these important to you?
- How comfortable are you with debt? This could include mortgage debt, credit card debt, and loans.
- Who should you spend money on? Do you agree on how much to give to your children or spend on gifts to family members, friends, or charities?
- What rules would you like to apply to purchases? For example, you might set a limit on how much one spouse can spend without consulting the other.
- Would you like to set aside some discretionary money for each of you? That could help you feel more free to save or spend those dollars without having to justify your decision.
What’s Your Money Style?
Agree on a plan
Once you’ve explored what’s important to you, create a concrete budget or spending plan that will help keep you on the same page. For example, to account for both perspectives, you could make savings an “expense” and also include a “just for fun” category. If a formal budget doesn’t work for you, find other ways to blend your styles, such as automating your savings or bill paying, prioritizing an emergency account, or agreeing to put specific percentages of your income toward wants, needs, and savings.
And track your progress. Scheduling money dates to go over your finances will give you a chance to celebrate your successes or identify what needs to improve. Be willing to make adjustments if necessary. It’s hard to break out of patterns, but with consistent effort and good communication, you’ll have a strong chance of finding the middle ground.
Copyright 2006- Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. All rights reserved.
Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. does not provide investment, tax, or legal advice. The information presented here is not specific to any individual’s personal circumstances.
To the extent that this material concerns tax matters, it is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, by a taxpayer for the purpose of avoiding penalties that may be imposed by law. Each taxpayer should seek independent advice from a tax professional based on his or her individual circumstances.
These materials are provided for general information and educational purposes based upon publicly available information from sources believed to be reliable—we cannot assure the accuracy or completeness of these materials. The information in these materials may change at any time and without notice.
*Non-deposit investment products and services are offered through CUSO Financial Services, L.P. (“CFS”), a registered broker-dealer (Member FINRA / SIPC) and SEC Registered Investment Advisor. Products offered through CFS: are not NCUA/NCUSIF or otherwise federally insured, are not guarantees or obligations of the credit union, and may involve investment risk including possible loss of principal. Investment Representatives are registered through CFS. Coastal Federal Credit Union has contracted with CFS to make non-deposit investment products and services available to credit union members.
CFS representatives do not provide tax or legal guidance. For such guidance please consult with a qualified professional. Information shown is for general illustration purposes and does not predict or depict the performance of any investment or strategy. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Trust Services are available through MEMBERS Trust Company. CFS* is not affiliated with Members Trust Company.